Picture this: it’s 2:30 a.m. You, your spouse, children, and newly adopted dog are sound asleep. Out of nowhere, you’re awoken by the sound and the fury of banging at your door. Doorbells don’t exist yet because it’s 1939. You only speak Polish, and four men dressed in military fatigues brandishing SS insignia who only speak German scream at you, barge into your home and forcefully relocate you to what appears to be a prison. You’re forced into a shower room with 100 other men, the tinge of a noxious smell hits your olfactory perception, and that is the last thing you ever feel. What did you do wrong, you wonder in your last moments. It turns out it was nothing more than the mezuzah on your door frame that gave you away. Sound familiar? This is what happened to over 6 million Jews during the Holocaust between 1939-45.
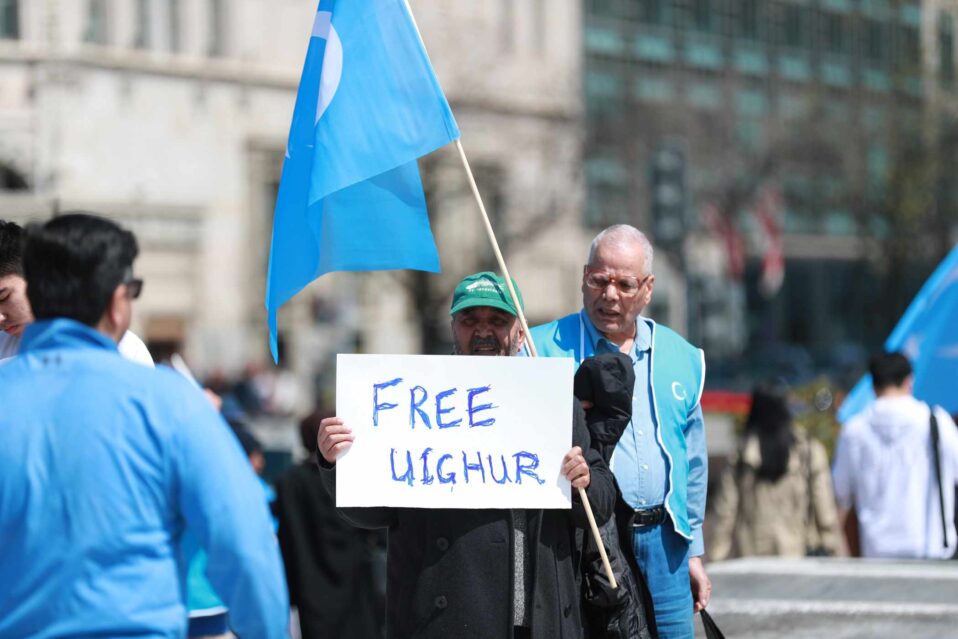
Close to a century later, a similar scenario is playing out in a largely unknown part of the world to a largely unknown group of people. Who are the Uyghurs, you may wonder. They are a minority Sunni Muslim group of Turkic origin totaling a global population of 11-12 million, primarily living in Xinjiang, China. Xinjiang is the most Northwestern province of China known for its austere environment and, contemporarily, the location of modern-day debatable genocide. But to understand what’s happening in Xinjiang, we must go back about 70 years.
After the defeat of the Kuomintang by Mao Zedong and the establishment of the Chinese Communist Party in 1949, the People’s Republic of China was established. However, the “People” in the title can be a little misleading. According to recent data, Statista shows that 89.43% of China is Han Chinese, with the remaining number being minority groups. Moreover, World Population Review estimates the current Chinese population is 1.425 billion people. This amounts to the Uyghur people accounting for only .772% of the Chinese population.
This means that the “People” in the People’s Republic of China belong to the Han Chinese people, with all outsiders being seen as a nuisance, burden, and unnecessary, much like the Jews in Nazi Germany. In the early 90s, with more and more Han Chinese settling in Xinjiang, a historically inhabited land by the Uyghurs, this naturally led to civil strife. Elizabeth Economy, a senior fellow at Stanford, details how the situation reached a boiling point in the 21st century. Beginning in the late 2000s, numerous terrorist attacks, mass killings, riots, and protests erupted in Xinjiang, resulting in the deaths of large numbers of Han Chinese. In 2014, China, under the leadership of Xi Jinping, the supreme despot of China, launched his “Strike Hard Campaign Against Violent Terrorism,” essentially turning Xinjiang into a police state ruled by a Gestapo-like group of what Mao would have labeled the Red Guards. Under this anti-terrorism campaign, many traditional Muslim traditions, including praying, were outlawed. Contemporaneously, the Xi regime began building large numbers of concentration camp-like facilities in Xinjiang and started imprisoning large numbers of minority Uyghurs.
China acknowledges the presence of these camps yet labels them “reeducation” camps aimed at reforming would-be terrorists into model Communists. According to numerous sources ranging from scholars Lindsay Maizland, writer for the Council on Foreign Relations, IGOs and NGOs, to include major institutions such as the UN and Amnesty International, and prominent journalists, including Philip Wen and Olzhas Auyezov of Reuters, one thing is for sure: A genocide is brewing in Xinjiang, China. According to all the previously mentioned sources, it is estimated that between 800,00 to 2,000,000 Uyghur people have been illegally imprisoned in the 385 detention facilities currently located in Xinjiang. Within the confines of these detention facilities, it has been reported that brutalities such as torture, forced sterilization, forced labor, and forced indoctrination into Chinese Communist ideology are commonplace,. The most challenging part, however, is proving it. Like George Orwell’s 1984, Xinjiang is one of the most Big Brother-like, heavily policed regions in the world. Xinjiang is also extremely austere, situated in a highly isolated and landlocked region of Asia largely inaccessible to the media. Moreover, China has severe restrictions on freedom of the press and access to social media and the internet, making it nearly impossible for local people to report the truth.
What is occurring in Xinjiang today parallels almost perfectly with what occurred in 1932 in Germany, with the death of Von Hindenburg and the rise of The Third Reich and Adolf Hitler. After the Great Depression, Adolf Hitler made great strides in recovering from the Depression through significant infrastructure projects (such as the Autobahn) and rebuilding the Wehrmacht (the German military). This came at the cost of seeking a scapegoat onto which to project society’s woes, in the former case, the Jews. Once Germany maintained its hegemonic status in continental Europe, it simply attempted to rid society of the scapegoat. Today, with the rise of the People’s Republic of China like a Phoenix from the ashes and the supreme leadership of Xi Jinping as the ultimate leader of the Chinese Communist Party, China too has its scapegoat onto which to cast its Mein Kampf-like ideologies. According to the Lowy Institute Asia Power Index, China ranks second in the world in comprehensive power and first globally in economic relationships and diplomatic influence. In simpler terms, China, with its global political influence, economic strength, and military prowess, will sooner rather than later reach and even overtake the U.S.’s hegemony on the world stage. Once this occurs, and China is given carte blanche to do anything that it feels. Through simple historical precedent, the Uyghur people will become yet another statistic in the Guinness World Record Genocide Fact Book.
Resolving this conflict diplomatically is the equivalent of asking Adolf Hitler, Idi Amin, Pol Pot, or Jefferson Davis to stop being mean to your minority populations. A hyper-extreme conservative state like China does not tolerate activists like Martin Luther King Jr or Gandhi. Individuals like them have no voice or ability to petition a draconian communist government with a redress of grievances. Additionally, nation-states with a dominant ethnic population and no significant obstacles preventing them from acting in an anti-social fashion toward minorities tend to engage in the universal art of ethnic cleansing. Saddam did it with the Kurds, the Ottomans with the Armenians, and even the pioneers with Native Americans.
The most realistic option to stymie an impending genocide could be to use whatever IGO, NGO, and Western political influence are left to attempt to relocate the Uyghur people to an ethnically similar, sovereign territory to China’s Northwest. Xinjiang lies on the border with Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan (all three being former parts of the Soviet Union, Sunni Muslim, and of Turkic and Persian ethnic origin). According to the CIA World Fact Book, 69.6% of Kazakhstan is ethnically Kazakhy (a Turkic ethnic group) and 70.2% Sunni Muslim. Kyrgyzstan is 73.8% Kyrg (a Turkic ethnic group) and 90% Sunni Muslim. And Tajikistan is 84.3% Tajik (a Persian ethnic group) and 95% Sunni Muslim. The assisted relocation of the Uyghurs would produce what, in science, is called a symbiotic effect. Symbiotic because it would mutually benefit both sides of the conflict. China would benefit by ridding a clearly unwanted ethnic group from its territory and preventing the continuation of ethnic Han and Uyghur clashes in Xinjiang. Conversely, the Uyghur people are saved from impending doom by relocating and inhabiting more friendly lands.
If this (pragmatically realistic) plan were to come to fruition, it would be one of the largest assisted mass migrations in history. Let us only hope that a 21st-century Muslim Moses exists that can help foster such an arduous undertaking and entreat China’s Pharaoh Ramses Jinping to let his people go.
Andrey Volfson is a MS candidate at Northeastern University in the Global Studies & International Relations program.
References:
Britannica, T. Editors of Encyclopaedia (2023, May 30). Uyghur. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/topic/Uyghur
China: CCP members by ethnic group 2021. Statista. (2022, July 1). https://www.statista.com/statistics/249994/number-of-chinese-communist-party-ethnic-minority-group-members-in-china/
China Population 2023. China population 2023 (live). (2023). https://worldpopulationreview.com/countries/china-population
Economy, E. (2022). The world according to China. Polity.
Maizland, L. (2022, September 22). China’s repression of
Uyghurs in Xinjiang. Council on Foreign Relations. https://www.cfr.org/backgrounder/china-xinjiang-uyghurs-muslims-repression-genocide-human-rights#:~:text=Most%20of%20the%20people%20who,sterilizations%2C%20among%20other%20rights%20abuses
Map – Australian strategic policy institute. The Xinjiang Data Project. (2021). https://xjdp.aspi.org.au/map/
BBC. (2022, May 24). Who are the Uyghurs and why is China being accused of genocide?. BBC News. https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-china-22278037
Maizland, L. (2022, September 22). China’s repression of Uyghurs in Xinjiang. Council on Foreign Relations. https://www.cfr.org/backgrounder/china-xinjiang-uyghurs-muslims-repression-genocide-human-rights
Wen, P., & Auyezov, O. (2018, November 27). Tracking China’s Muslim Gulag. Reuters. https://www.reuters.com/investigates/special-report/muslims-camps-china/
Central Intelligence Agency. (2023, June 15). Kazakhstan. Central Intelligence Agency. https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/kazakhstan/#people-and-society
Central Intelligence Agency. (2023b, June 20). Kyrgyzstan. Central Intelligence Agency. https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/kyrgyzstan/#people-and-society
Central Intelligence Agency. (2023c, June 20). Tajikistan. Central Intelligence Agency. https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/tajikistan/#people-and-society